Bolts and nuts should be selected to conform to the design specifications set out with the flange design. Care is taken to ensure that the correct grade of material is selected to suit the recommended bolting temperature and stress ranges. Material specifications for bolts are outlined in BS 4882 and ASME Section VIII.
Common material specifications for bolts and nuts are shown in Table A.
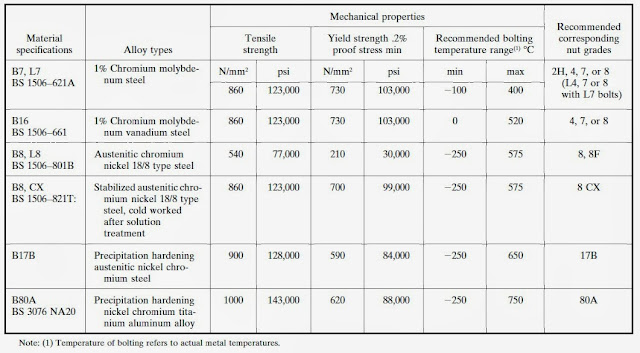 |
| Material Specifications for Bolts and Nuts and Recommended Bolting Temperature Range |
The following information should be specified when ordering bolts and nuts:
1. Quantity
2. Grade of material, identifying symbol of bolt or nut
3. Form
● Bolts or stud-bolts
● Nuts, regular or heavy series
4. Dimensions
● Nominal diameter, length
● Diameter of plain and reduced portion, length of thread (if applicable)
5. Identification of tests in addition to those stated in the standard
6. Manufacturer’s test certificate (if required). Fully threaded studbolts and heavy series nuts are most common in industrial applications.
High Temperature Bolting Applications
The relaxation of bolt stress under constant strain conditions is widely recognized and has been measured in research on studbolt assemblies. At temperatures in excess of 300 C, special steels and alloys are required to improve upon the stress relaxation performance of low alloy steels. The relaxation behaviors of different bolting materials are shown in Fig. A.
Different nut materials influence the stress-relaxation behavior of the stud, nut assembly. The recommended nut for each grade of stud is shown in Table A.
High temperature relaxation is a combined effect of gasket creep, bolt creep, and flange rotation. All three or any combination may occur. The symptoms show up as loose bolts that reduce gasket stress, resulting in increased leakage.
Tagged as :
PandID
Pipelines
Piping
Piping Design



0 comments :
Post a Comment